Specialist
Metal Patina
&
Colouring
BHA Architectural Metalwork Ltd offer professional surface preparation services
for a variety of metals.
A uniqely aged metal finish
Antique Brass, Weathered Copper, Verdigris and Black Stainless Steel.
What is Patination?
Patina on metal is a thin layer that variously forms on the surface (tarnish produced by oxidation or other chemical processes). The most common example of which is rust which forms on iron or steel when exposed to oxygen. Another, is verdigris, a green or blue powdery patina that forms on copper and bronze. Resulting from the slow chemical reaction of copper with carbon dioxide, producing copper carbonate. A patina takes many years to develope under natural weathering conditions.
Speciality patination of:
- Brass
- Bronze
- Copper
- Stainless Steel
- Mild Steel
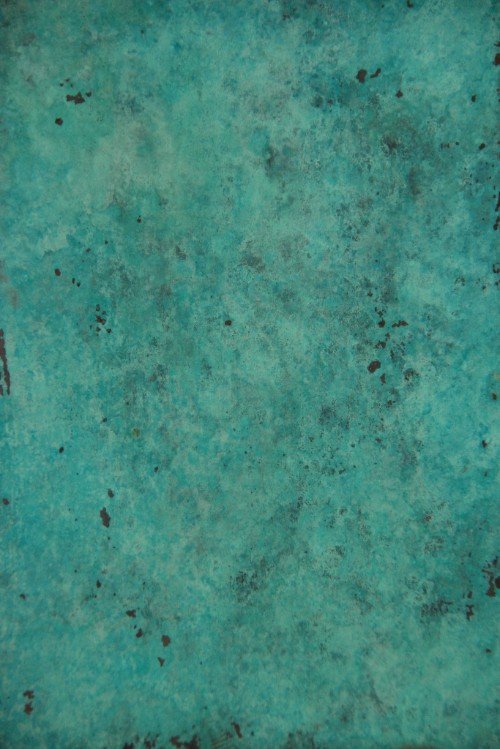

Patination is used to enhance the look of the metal. We use a range of different chemicals to create a variety of patinas.Patina can be used to simulate antiquity, add colour, create texture, enhance and uniquely individualise the metalwork. We use a microcrystalline wax to seal the patina and buff to a high shine finish.